Battery working principle
The electrochemical reaction principle of lead-acid battery is that electrical energy is converted into chemical energy and stored in the battery when charging, and chemical energy is converted into electrical energy and supplied to the external system when discharging. Its charging and discharging process is completed by electrochemical reaction, electrochemical reaction formula is as follows:
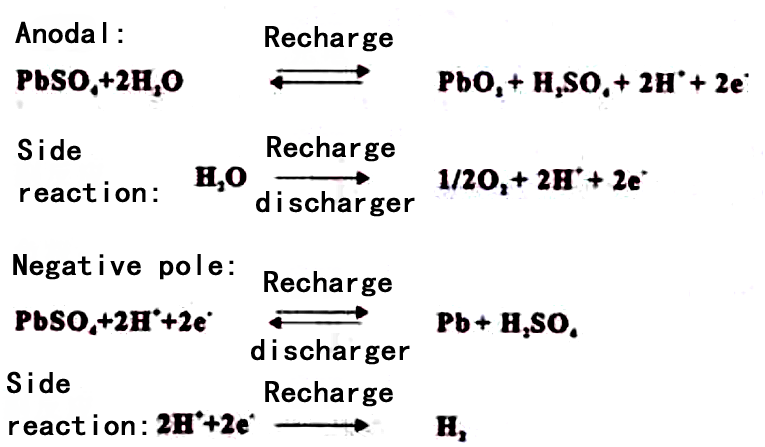
From the reaction formula can be seen, there is water decomposition reaction in the charging process, when the positive electrode charging to 70%, began to precipitate oxygen, negative electrode charging to 90% began to precipitate hydrogen, due to the precipitation of hydrogen and oxygen, if the reaction of the gas can not be re-compound to be used, the battery will lose water to dry up; for the early traditional lead-acid batteries, due to the precipitation of hydrogen and oxygen and from the internal escape of the battery, can not be carried out gas re-compound, it is necessary to frequently add acid to add the gas to the battery, it is necessary to frequently add acid to the battery, it is necessary to frequently add acid to the battery. Compound, is often need to add acid and water maintenance is an important reason; and valve-regulated lead-acid batteries can be in the battery on the oxygen re-compound utilization, while inhibiting the precipitation of hydrogen, to overcome the main shortcomings of the traditional lead-acid batteries.

Lead-acid battery adopts negative active material excess design, AG or GEL electrolyte adsorption system, the oxygen generated in the late charging period of positive electrode diffuses to the negative electrode through the AGM or GEL gap, and reacts with the negative electrode spongy lead to become water, so that the negative electrode is in the state of depolarization or insufficient charging, and reaches the overpotential of precipitation of hydrogen, so the negative electrode won't precipitate hydrogen due to the charging, and the battery loss is very small, so it doesn't need to add acid and water for maintenance during the period, so it is not necessary to add acid and water for maintenance. Therefore, there is no need to add acid and water for maintenance. The oxygen cycle of valve-regulated lead-acid battery is shown as follows:
It can be seen that in the lead-acid battery, the negative electrode plays a double role, that is, at the end of charging or overcharging, on the one hand, the spongy lead in the pole plate reacts with the O2 produced by the positive electrode and is oxidized into lead monoxide, and on the other hand, the lead sulphate in the pole plate should be oxidized into lead monoxide.
On the other hand, the lead sulfate in the polar plate has to accept the electrons transmitted from the external circuit to carry out the reduction reaction, and the lead sulfate reacts to spongy lead.